Featured Article
WiFi Mesh Networks vs. WiFi Extenders
In the modern home, a strong and reliable internet connection is essential for everything from working remotely to streaming movies or playing games.
But many homeowners struggle with weak or spotty WiFi signals. To solve this, you have two options: WiFi mesh networks or WiFi extenders. In this post, we'll break down why WiFi mesh networks are far superior to WiFi extenders, especially when it comes to delivering reliable, seamless coverage throughout your entire home.
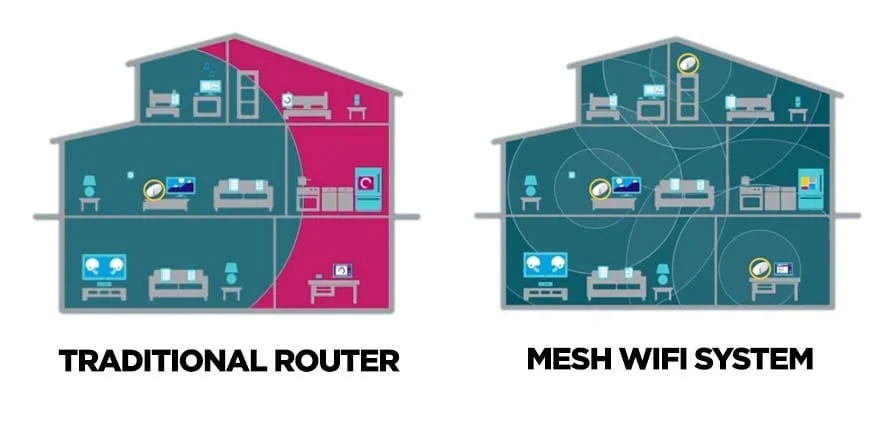
How a Traditional Single-Point Router Works
Most homes start with a single-point WiFi router. This router connects to your modem and broadcasts a wireless signal that extends out from its central location. In smaller homes or apartments, a single router may be enough to cover the entire space. However, as the size of your home increases—or if you have thick walls or multiple floors—the router’s signal weakens as you move farther away from it. This can lead to dead zones, slow speeds, and general frustration.
To tackle these issues, homeowners often explore ways to extend the range of their WiFi network by adding more WiFi radio nodes. This is where the distinction between WiFi extenders and WiFi mesh networks comes into play.
WiFi Extenders
WiFi extenders are often the first solution people try when they experience dead zones. These devices connect to your main router and essentially “boost” or “extend” the signal to areas that the router can't reach. However, they don’t strengthen the original signal. They simply rebroadcast it, which can come with several downsides:
- Separate networks: Many WiFi extenders create a new, separate WiFi network. So instead of having a single, seamless network in your home, you end up with two (or more) networks. For example, you might have “HomeWiFi” and “HomeWiFi_EXT.”
- Manual switching: Because extenders broadcast a different network, you often have to manually switch between the router and extender networks as you move around your home. This leads to connection interruptions, especially with devices like smartphones or laptops that don’t automatically handle switching well.
- Amplification of an already weak signal: Since the WiFi range extender is catching the already weak signal coming from your router, the signal from the range extender will likely also have a slow internet speed.
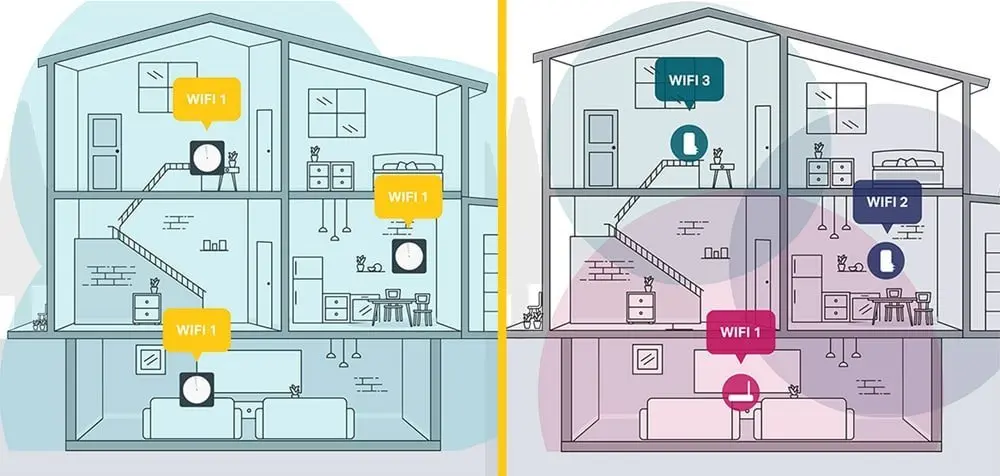
Since most extenders create a separate WiFi network, you'll have to manually switch between the two networks as you move around your house. Your device won't automatically switch to the stronger signal unless the weaker one is almost lost. This can result in your device being stuck on a weaker network, sometimes worse than before installing the extender.
Some extenders allow you to set the same network name (SSID) for both the extender and the router. For these extenders you'd expect your device to seamlessly switch between them based on signal strength, but the WiFi standard typically prevents this from working well. Devices tend to cling to the original access point they connect to, even if a stronger signal becomes available. For example, if your device first connects to your router and you move closer to the range extender with a stronger signal, it may still stick to the weaker router signal. This defeats the purpose of the extender. Additionally, using an extender with a router of a different WiFi generation (like WiFi 5 and WiFi 6) or with different antenna configurations can make the problem worse.
WiFi Mesh Networks
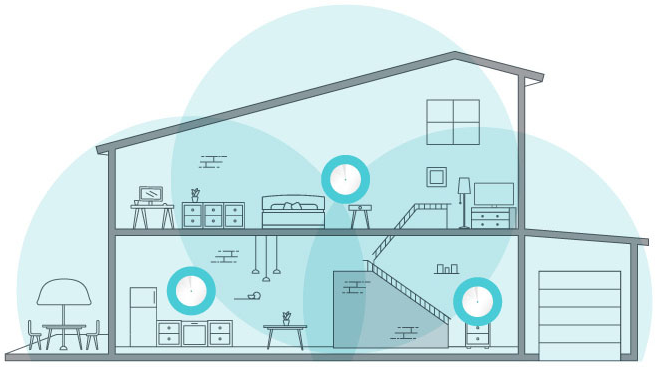
WiFi mesh networks offer a more modern and elegant solution to extending your WiFi range—and they do so in a way that avoids the pitfalls of extenders. A mesh system consists of multiple nodes, or “satellites,” that work together to create a single, unified WiFi network throughout your home. Rather than simply extending the signal from one router, mesh nodes communicate with each other to distribute the signal evenly and efficiently across your entire space.
WiFi mesh networks are superior to range extenders in several key ways:
- Single unified network: With a mesh system, you only have one WiFi network name (SSID), no matter where you are in your home. This creates a seamless experience, with your device automatically connecting to the nearest node with the strongest signal. You don’t have to worry about switching between networks or dealing with dropped connections as you move around.
- Consistent speed and coverage: Each node in a mesh system works as part of a single, intelligent network. Mesh networks dynamically route traffic between nodes to ensure that each device gets the best possible connection. If one node becomes overloaded or weak, the system can automatically redirect traffic through other nodes, maintaining consistent speeds throughout your home.
- Seamless roaming: One of the most significant advantages of mesh networks is seamless roaming. As you move through your home, your device will automatically connect to the node with the strongest signal without any interruptions. Whether you’re walking from the living room to the upstairs bedroom or moving around during a video call, the mesh system ensures that your connection remains stable and strong.
- Scalability and flexibility: Mesh systems are easily scalable. You can add more nodes to your system as needed, whether you're expanding to a larger home or improving coverage in tricky areas like basements or outdoor spaces.
- Separate frequency for backhaul traffic: Mesh networks will place the backhaul traffic (the traffic that flows between the nodes) on an entirely different frequency. Therefore, freeing up bandwidth for your phones and computers.
Final Verdict: Why Mesh Networks Win
WiFi extenders can offer a quick fix for small dead zones, but they are a band-aid solution with significant limitations. For homes with a need for consistent, high-speed internet throughout, mesh networks are the clear winner.
If you're serious about improving your home network's performance, a mesh system will provide the reliability and flexibility you need, ensuring that your WiFi is strong, fast, and always connected, no matter where you are in your home.